The American Russell Index 2000, referred to as “Russell 2000”, is called “Russell 2000” in English. The index was founded by Frank Russell Company in 1984 and is now managed by FTSE Russell, a subsidiary of the London Stock Exchange Group. The US Russell Index 2000 is composed of the 2,000 companies with the smallest market capitalization in the Russell 3000 Index (covering 98% of the total market capitalization of US stocks). The total market capitalization is approximately 10% of the Russell 3000 Index. The index is mainly used to measure the performance of small and medium-sized enterprises listed in the United States.
The US Russell Index 2000 is a market capitalization-weighted index. As of March 31, 2020, the average market value of the 2000 companies in the index is US$2.053 billion, the median market value is US$490 million, and the maximum market value is US$11.220 billion. In contrast, the average market value of the companies included in the Dow is 277.73606 billion US dollars. It can be seen that the companies covered by the US Russell Index 2000 are all smaller companies.
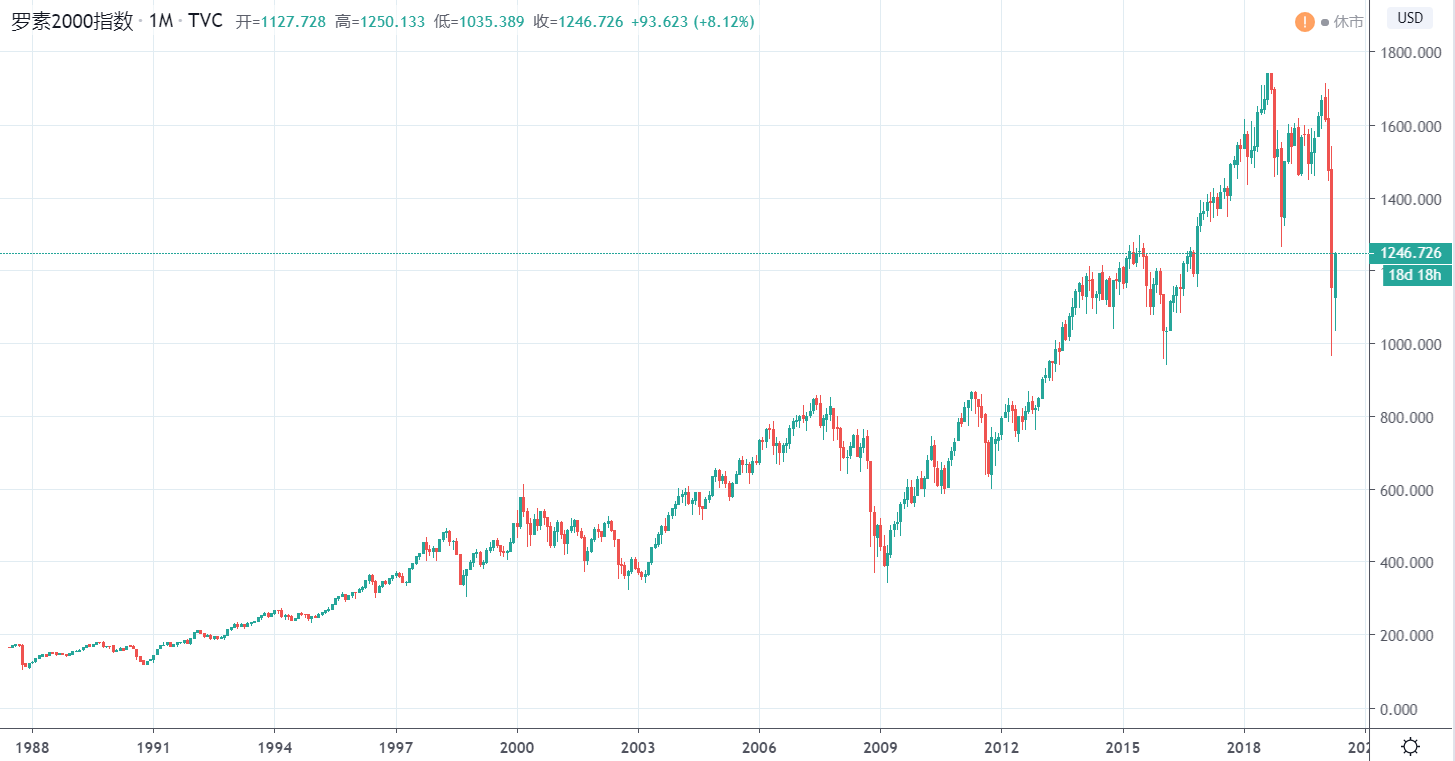
US Russell Index 2000 is sometimes compared with the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index. The former represents small companies and the latter represents large companies. Many people think that the market value of small companies must fluctuate more than that of large companies. That is, the volatility of Russell 2000 is greater than that of the S&P 500. This is true after 2000, but before 2000, the volatility of Russell 2000 was smaller than that of the S&P 500’s.
There is also no absolute relationship between the yields of the two. From the perspective of historical trends, the yield of Russell 2000 is lower than the S&P 500 during economic booms (such as from 2014 to 2019), but in periods of economic instability (such as flooded with 9/11), The Iraq War, and the subprime mortgage crisis from 2000 to 2014), Russell 2000’s yield was greater than that of the S&P 500.

 IronFX
IronFX
Comment by Diletta
March 26, 2024
Awesome bonuses, good leverage. A few hiccups, but support rocks!